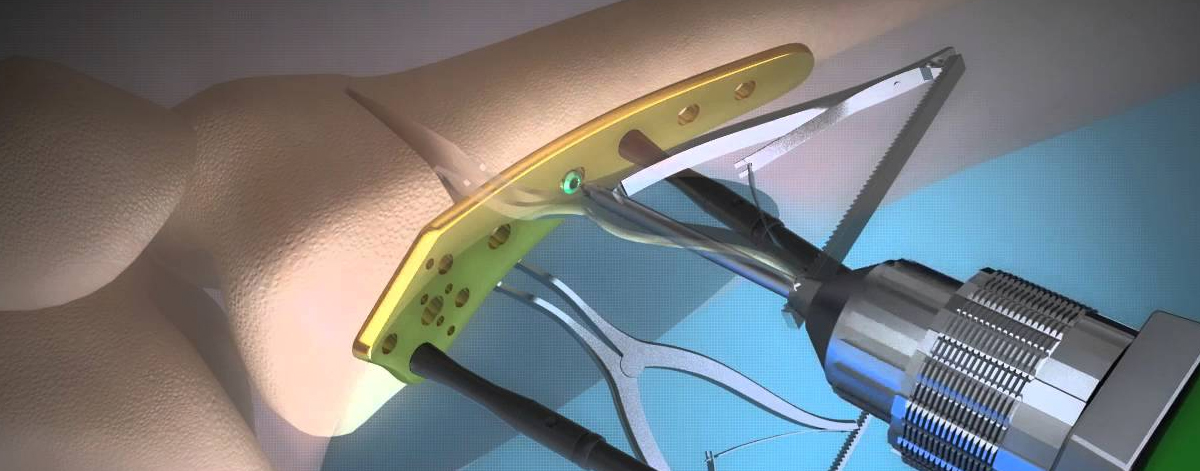
Distal Femur Osteotomy
Distal femur osteotomy is a surgical procedure that involves cutting and repositioning the lower part (distal) of the femur (thigh bone) to realign the knee joint. This procedure is typically performed to treat certain knee conditions, such as knee malalignment, angular deformities, or early-stage osteoarthritis affecting the knee joint. The goal of distal femur osteotomy is to shift the weight-bearing load across the knee joint, reduce pain, and improve joint function, thus delaying or avoiding the need for knee replacement surgery.
The surgery is often indicated when there is an abnormal alignment of the lower limb, such as genu valgum (knock-knees) or genu varum (bowlegs), which can lead to uneven wear on the knee joint and cause pain, instability, and reduced mobility. Distal femur osteotomy can help correct these angular deformities and realign the knee joint, leading to more even distribution of forces across the joint.
The Distal Femur Osteotomy Procedure:
- Anesthesia: The surgery is performed under general anesthesia or regional anesthesia, depending on the patient's condition and the surgeon's preference.
- Incision: The surgeon makes an incision over the lower part of the femur to access the bone.
- Bone Cut: A carefully planned bone cut (osteotomy) is made in the distal femur to change its alignment. The surgeon adjusts the alignment based on the specific knee condition and the desired correction.
- Fixation: Once the desired realignment is achieved, the bone segments are held in place with specialized metal plates, screws, or external fixation devices. These implants provide stability while the bone heals in its new position.
- Closure: After ensuring proper alignment and fixation, the incision is closed with stitches or staples.
Do's for Distal Femur Osteotomy
- Follow Pre-operative Instructions: Adhere to your surgeon's pre-operative guidelines, which may include fasting instructions, medication restrictions, and hygiene protocols.
- Prepare Your Home: Make sure your home is safe and accessible for your recovery, with clear pathways and assistive devices like crutches or a walker.
- Comply with Medications: Take prescribed medications, including pain relievers and antibiotics, as directed to manage pain and prevent infections.
- Keep the Incision Clean and Dry: Follow your surgeon's instructions on caring for the surgical incision to prevent infections and promote proper healing.
- Control Swelling and Pain: Use ice packs and elevation to control swelling, and take pain medications as prescribed to manage discomfort.
Don'ts for Distal Femur Osteotomy
- Overexert Yourself: Avoid putting excessive stress on the healing knee during the early stages of recovery. Follow your physical therapist's guidelines and gradually increase activity as advised.
- Neglect Physical Therapy: Continue with your physical therapy sessions diligently to ensure a successful recovery and improve knee function.
- Ignore Signs of Infection: If you experience signs of infection, such as fever, increased redness, swelling, or drainage from the incision, contact your surgeon immediately.
- Engage in High-Impact Activities: Avoid high-impact exercises or activities that may put excessive strain on the healing knee.
- Sit for Prolonged Periods: Avoid sitting or lying in one position for too long to prevent stiffness and discomfort.