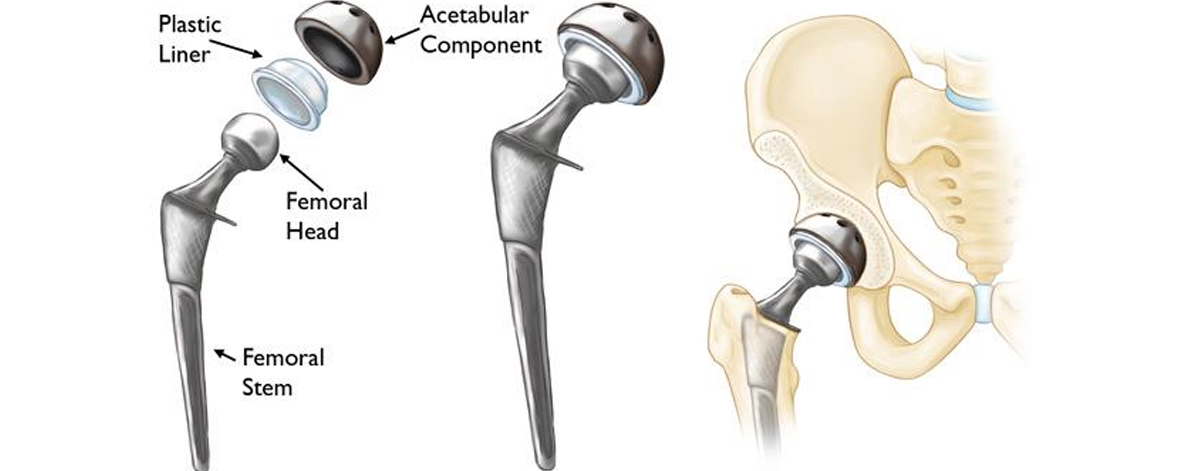
Hip Replacement
Hip osteoarthritis replacement refers to the surgical procedure of replacing the damaged hip joint with an artificial joint, known as a prosthesis. This procedure is also known as total hip replacement (THR) and is considered one of the most effective treatments for end-stage hip osteoarthritis when other conservative measures are no longer sufficient to manage the pain and disability associated with the condition.
Do's for Hip Replacement
- Follow Pre-operative Instructions: Adhere to your surgeon's pre-operative guidelines, which may include fasting instructions, medication restrictions, and hygiene protocols.
- Prepare Your Home: Make sure your home is safe and accessible for your recovery, with clear pathways and assistive devices like a walker or cane.
- Comply with Medications: Take prescribed medications, including pain relievers and antibiotics, as directed to manage pain and prevent infections.
- Keep the Incision Clean and Dry: Follow your surgeon's instructions on caring for the surgical incision to prevent infections and promote proper healing.
- Control Swelling and Pain: Use ice packs and elevation to control swelling, and take pain medications as prescribed to manage discomfort.
Don'ts for Hip Replacement
- Overexert Yourself: Avoid putting excessive stress on the new hip joint during the early stages of recovery. Follow your physical therapist's guidelines and gradually increase activity as advised.
- Neglect Physical Therapy: Continue with your physical therapy sessions diligently to ensure a successful recovery and improve hip function.
- Ignore Signs of Infection: If you experience signs of infection, such as fever, increased redness, swelling, or drainage from the incision, contact your surgeon immediately.
- Engage in High-Impact Activities: Avoid high-impact exercises or activities that may put excessive strain on the hip joint.
- Sit for Prolonged Periods: Avoid sitting or lying in one position for too long to prevent stiffness and discomfort.